Optimization of a cogeneration plant
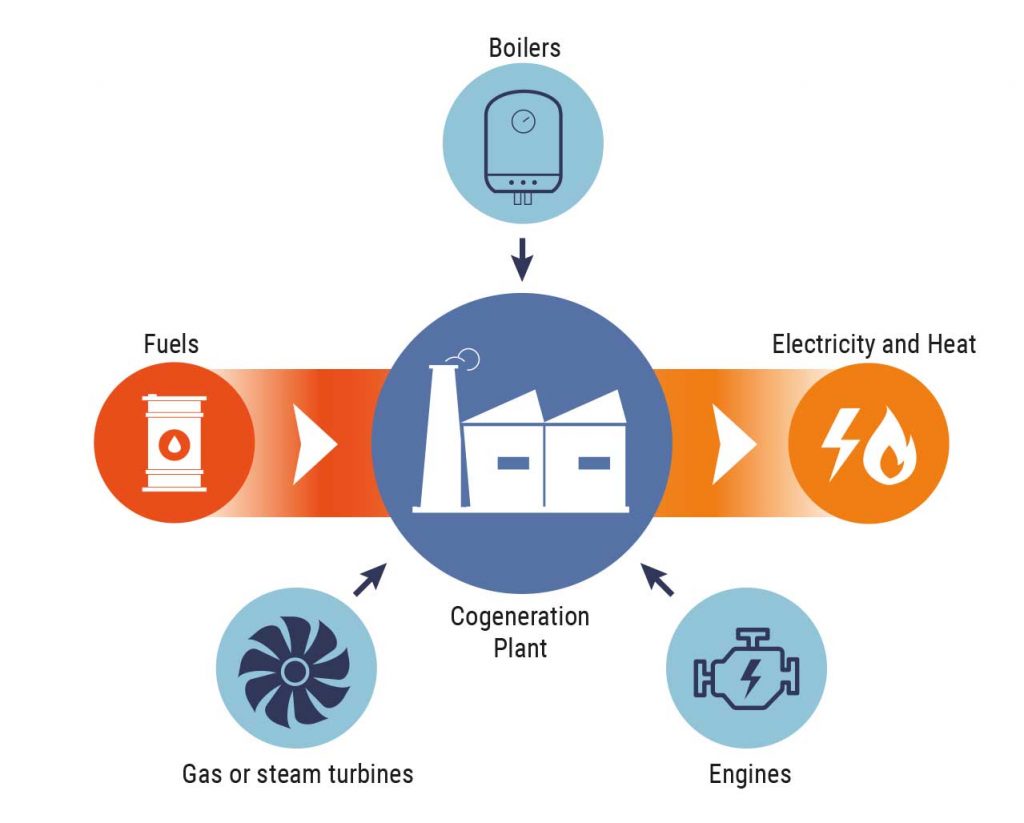
Cogeneration is the process of simultaneously producing electricity and heat through the concurrent utilization of turbines, engines, boilers or other instruments. The energy and heat generated can be used for heat, steam, and/or for production-industrial processes.
The principle of cogeneration
Some examples of applications of the cogeneration process include power plants, refineries, chemical plants, food and pharmaceutical companies, incinerators, paper mills, sugar refineries, sawmills, institutions (schools, hospitals, prisons, college campuses) and plants powered by peat and wood waste.
Maximize efficiency of a cogeneration plant
To maximize the yield of such plants, it is obviously necessary to monitor fuel consumption, combustion efficiency and the level of emissions.
These checks are also essential for the maintenance and safety of the plant and can be carried out with emissions gas analyzers that permit verification of the temperature of the gases and their concentrations.
In particular, the gases concerned are O₂, CO and CO₂, CxHy, total NOx (NO + NO₂), SO₂ and H₂S (amongst others).
Seitron instrumental solution
The solution proposed by Seitron is the emissions analyzer S9000, capable of carrying out accurate measurements of the gases in question and equipped with dedicated software for data recording and analyses.
The S9000 features:
- TFT color display
- Optional heated sample line
- Up to 9 sensors + 3 on NDIR bench
- Field replaceable sensors
- Mobile app for iOS, Android
- PC software


Are you interested to know more? Contact us!
Download the full pdf version: Optimization of a cogeneration plant